ADMX Technology Review
In Windows Vista or later, ADMX files are divided into language-neutral and language-specific resources, available to all Group Policy administrators. These factors allow Group Policy tools to adjust their UI according to the administrator’s configured language. Adding a new language to a set of policy definitions is achieved by ensuring that the language-specific resource file is available.
Comparison of ADM and ADMX Local File Locations
In Windows Vista beta 2, the operating system–defined Administrative Template policy settings will only install on the local computer as an ADMX file format.
ADMX files will be installed on each Windows Vista computer in a different file location from ADM files, as shown in the following table.
(Custom ADM files can still be copied to the listed ADM directory to be consumed by the Group Policy Object Editor and Group Policy Management Console.)
| File Type | File Location |
|---|---|
| ADM | %systemroot%\inf |
| ADMX language neutral (.admx) | %systemroot%\policyDefinitions |
| ADMX language specific (.adml) | %systemroot%\policyDefinitions\[MUIculture] (for example, the U.S. English ADMX language specific file will be stored in %systemroot%\policyDefinitions\en-us) |
ADMX Domain File Locations
One of the main benefits of using the new ADMX files is the central store. This option is available to you when you are administering domain-based GPOs, although the central store is not used by default. In Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, the Group Policy Object Editor will not copy ADM files to each edited GPO—the case with earlier operating systems. Instead the Group Policy Object Editor will no longer copy the new ADMX files, but will provide the ability to read from either a single domain-level location on the domain controller sysvol (not user configurable) or from the local administrative workstation when the central store is unavailable. This capability reduces the amount of storage needed for files that should remain constant for all GPOs. In addition to storing the ADMX files shipped in the operating system in the central store, you can share a custom ADMX file by copying the file to the central store, which makes it available automatically to all Group Policy administrators in a domain.
| File Type | Domain Controller File Location |
|---|---|
| ADMX language neutral (.admx) | %systemroot%\sysvol\domain\policies\PolicyDefinitions |
| ADMX language specific (.adml) | %systemroot%\sysvol\domain\policies\PolicyDefinitions\[MUIculture] (for example, the U.S. English ADMX language-specific file will be stored in %systemroot%\sysvol\domain\policies\PolicyDefinitions\en-us) |
Requirements for Editing Group Policy Objects with ADMX Files
The following sections describe specific computer setups required for editing either the local GPO or domain-based GPOs with ADMX files. This step-by-step guide assumes you understand the basic concepts of Group Policy and using the Group Policy Management Console.
Local Group Policy Object Editing Requirements
While editing the local GPO, you must use a Windows Vista-based computer to view policy settings from ADMX files.
Domain-Based Group Policy Object Editing Requirements
In order to be able to create and edit domain-based GPOs with the latest Group Policy settings using ADMX files, you must have this setup:
- A working Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2003, or Windows 2000 domain using name resolution through a DNS server.
- A Windows Vista computer to view policy settings from ADMX files while editing the domain-based GPO.
ADMX Scenarios
The scenarios in this document are designed to introduce you to managing ADMX files for Group Policy editing. (Group Policy editing refers to the process in which you create a GPO or open an existing GPO and then change policy settings using the Group Policy Object Editor). The following two scenarios illustrate how the Group Policy Object Editor will transparently incorporate ADMX files into an editing session. The domain-based scenario shows you how to centrally manage ADMX files, a feature that was not available with ADM files.
Scenario 1: Editing the Local GPO with ADMX Files
This scenario shows you how ADMX files are transparently incorporated into editing the local Group Policy.
Editing the Administrative Template Policy Settings of the Local GPO with ADMX files
You must use a Windows Vista-based computer to edit local GPOs using ADMX files.
To edit administrative template policy settings using ADMX files
- To open the local Group Policy Object Editor on a Windows Vista machine, click Start, click Run, then type GPEDIT.msc.
- The Group Policy Object Editor will automatically read all ADMX files stored in the %systemroot%\PolicyDefinitions\ folder.
- Locate the policy setting you wish to edit and open it.
Note You can still remove and add ADM files to the GPO using the Add/Remove Templates menu option. There is no user interface for adding or removing ADMX files in Windows Vista.
To add ADMX files to the Group Policy editing session, copy the ADMX files to the %systemroot%\PolicyDefinitions\ folder and restart the Group Policy Object Editor.
Scenario 2: Editing Domain-Based GPOs with ADMX Files
This scenario shows you how to set up a central location of the updated ADMX files when managing domain-based Group Policy from Windows Vista–based computers.
Steps for Utilizing the Optional ADMX Central Store with Domain-Based GPOs
Prerequisites for Administering Domain-Based GPOs with ADMX Files
To complete the tasks in this section, you should have at least:
- A Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2003, or Windows 2000 domain utilizing a DNS name server.
- A Windows Vista-based computer to use as an administrative workstation.
If you choose to not create an ADMX central store, editing GPOs will work the same way as in Scenario 1: Editing the Local GPO with ADMX Files. To edit GPOs using centrally stored ADMX files, complete these tasks in order.
Create a Central Store
The central store is a folder structure created in the sysvol directory on the domain controllers in each domain in your organization. You will need to create the central store only once on a single domain controller for each domain in your organization. The File Replication service then replicates the central store to all domain controllers. It is recommended that you create the central store on the primary domain controller because the Group Policy Management Console and Group Policy Object Editor connect to the primary domain controller by default.
The central store consists of a root-level folder containing all language-neutral ADMX files and subfolders containing the language-specific ADMX resource files.
To perform this procedure, you must be a member of the Domain Admininstrators group in Active Directory.
Steps To create the central store
- Create the root folder for the central store %systemroot%\sysvol\domain\policies\PolicyDefinitions on your domain controller.
- Create a subfolder of %systemroot%\sysvol\domain\policies\PolicyDefinitions for each language your Group Policy administrators will use. Such as EN-US, EN-GB.etc.
Note Each subfolder is named after the appropriate ISO-style Language/Culture Name. For a list of ISO-style Language/Culture Names, see Valid Locale Identifiers. For example, to create a subfolder for U.S. English, create the subfolder: %systemroot%\sysvol\domain\policies\PolicyDefinitions\EN-US
Populate the Central Store with ADMX Files
There is no user interface for populating the central store in Windows Vista. The procedure shows how to populate the central store using command line syntax from the Domain Controller.
To populate the central store
- Open a command window: click Start, click Run, then type cmd.
- To copy all the language-neutral ADMX files from your Windows Vista administrative workstation to the central store on your domain controller using the xcopy command, type:
xcopy %systemroot%\PolicyDefinitions\* %logonserver%\sysvol\%userdnsdomain%\policies\PolicyDefinitions\ - To copy all ADMX language resource files from your Windows Vista administrative workstation to the central store on your domain controller using the xcopy command, type:
xcopy %systemroot%\PolicyDefinitions\EN-US\* %logonserver%\sysvol\%userdnsdomain%\policies\PolicyDefinitions\EN-US\
To edit administrative template policy settings using ADMX files
- To open the Group Policy Management Console on a Windows Vista machine, click Start, click Run, then type GPMC.msc.
- To create a new GPO to edit, right-click the Group Policy objects node and select New.
- Type a name for the GPO and click OK.
- Expand the Group Policy objects node.
- Right-click the name of the GPO you created and click Edit.
- The Group Policy Object Editor automatically reads all ADMX files stored in the central store.
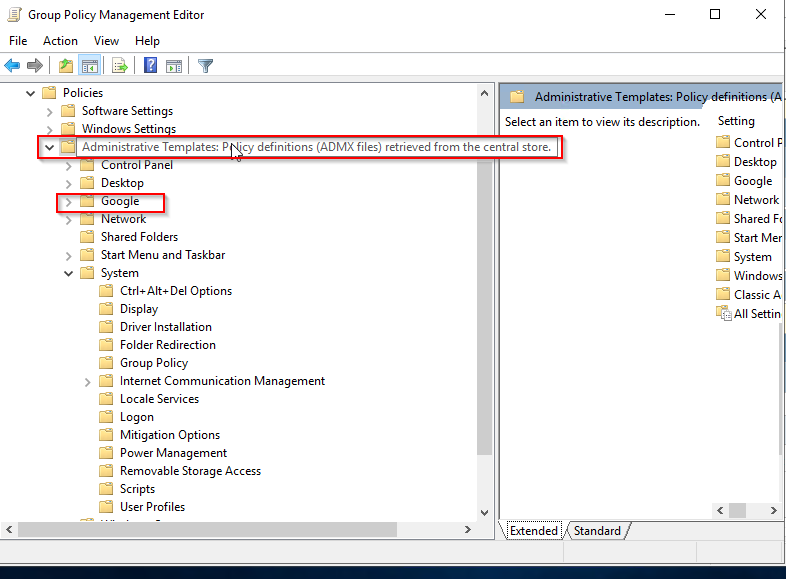
When there is no central store, the Group Policy Object Editor reads the local versions of the ADMX files used by the local GPO on your Windows Vista administrative machine. Go to the Computer configuration > Policies > Administrative Tempalates > The_ADMX file name (eg. google).
To verify it’s setup successfully
Open Group Policy Management Editor, go to the Administrative Templates, it will take slightly more time to load, you will see ” Policy definitions(ADMX files) retrieved from the central store”
Note You can still remove and add ADM files to the GPO. There is no user interface for adding or removing ADMX files in Windows Vista.
To add local ADMX files to the Group Policy editing session, copy the ADMX files to the %systemroot%\PolicyDefinitions\ folder and restart the Group Policy Object Editor.