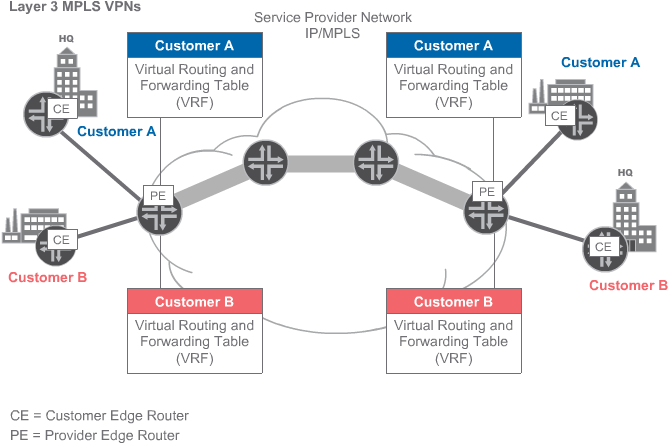
MEF Three-layer Model
The Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF) Three-Layer Model for Carrier Ethernet is somewhat like a collapsed version of the Five-Layer Reference Model referred to in this course. The three layers are as follows:
– Application Services Layer
– Ethernet Services Layer
– Transport Services Layer
Each layer has its own data, control, and management planes.
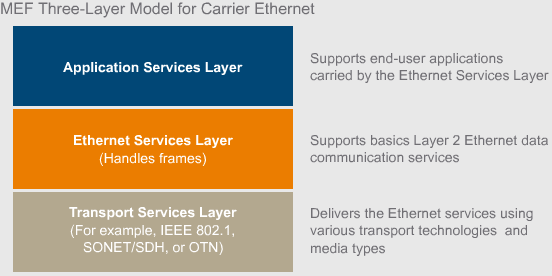
Three different Plane:
Date plane: handles data according to logic in place.
Control plane: Instructs data plane on how to process data.
Management Plane: administrative interface allowing for configuration.
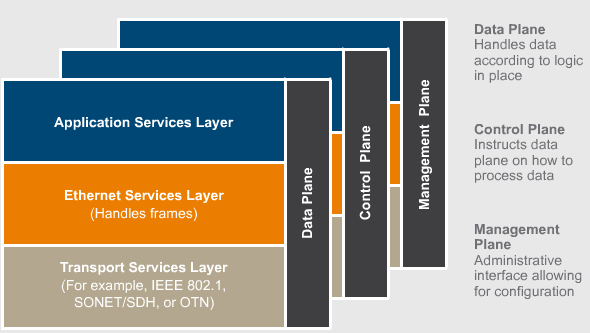
Multi-Protocol label Switching(MPLS)
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a data packet forwarding technology used to improve the forwarding speed of routers by using labels to make forwarding decisions. When a packet enters the MPLS network, the first MPLS router adds a simple label based on fields in the IP header. Routers within the MPLS network forward the packet based on the contents of the label. MPLS is often referred to as a Layer 2.5 protocol because it operates between Layer 2 and Layer 3, is Layer 2-independent, provides the privacy and security of a Frame Relay or ATM network, and yet allows for the inherent
any-to-any connectivity and flexibility typical of an IP-based network.
It provides the privacy and security of a Frame Relay or ATM network, yet allows for the inherent any-to-any connectivity and flexibility typical of an IP-based network.
Label Switched Paths (LSPs) are the unidirectional paths used to connect each location in an MPLS network. Each LSP must be matched with another in the opposite direction.
Label Switching Routers (LSRs) are routers running the MPLS protocol.
An MPLS domain is an MPLS network.
A Label Edge Router (LER) is a special type of ingress or egress LSR that is responsible for assigning the appropriate MPLS label to a packet.
LER assigns labels based on:
- Destination IP network;
- Destination IP network and application type
- Source and destination IP network
- Specific QoS requirement.
A Forwarding Equivalency Class (FEC) is a group of packets that the provider’s MPLS domain forwards and treats the same.
Transit LSRs are routers that only examine the MPLS label on a packet.
MPLS header
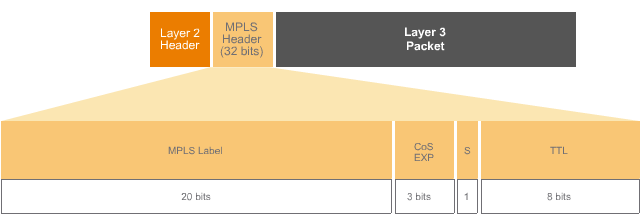
MPLS label(20 bits): Contains a locally significant value specifying the packet belongs to a certain LSP.
Cos_experimental Bits(3 bits): Now they are used as the class of service(Cos) which are used for QoS in an MPLS network.
S_Bottom of stack bit(1 bit): A packet can have multiple labels, this bit indicates whether an IP packet or another MPLS header follows the current MPLS header. If the bit is set to one, an IP header is next. If it is set to zero, another MPLS header follows.
TTL(8bit):
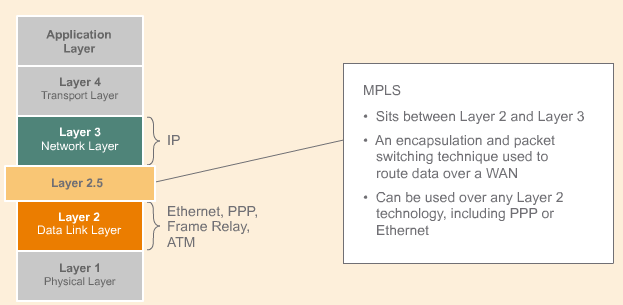
MPLS VPNs
Layer 3 MPLS VPNs or IP VPNs:
Layer 3 MPLS VPNs or IP VPNs define a way for providers to use their IP backbone to provide IP-based VPN services regardless of what Layer 2 technology is in use. Layer 3 MPLS VPNS use label switched paths to interconnect different customer locations and keep traffic separated. Customer edge routers exchange IP routing information with the provider’s routers where it is stored in a virtual router and forwarding table. Provider Edge routers exchange routes with other provider edge routers within the VPN. When IP packets enter the MPLS network, the provider edge router determines which LSP to use to based on the routing information in the virtual router and forwarding table .
Customer Edge(CE) router:
A Customer Edge (CE) router is a router at the customer’s site that uses a single physical connection to connect to a Provider Edge router in the provider’s MPLS network using any Layer 2 protocol. The CE router is at the edge of the customer’s MPLS VPN even though the CE router does not run the MPLS protocol.
Provider Edge(PE) router:
A Provider Edge (PE) router is a type of edge router used in MPLS VPNs, and must provide completely private and secure connectivity within a VPN. PE routers also exchange routing information with customer edge routers and other PE routers within the VPN. The PE routers store the customer’s routing information in a Virtual Routing and Forwarding table or instance.
The provider edge router stores each customer’s routing information in a Virtual Routing and Forwarding table or instance, which is known as a VRF.
Virtual Routing and Forwarding(VRF)
A Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) table or VRF instance is a repository on an MPLS Provider Edge router where customer routing information is stored. VRFs are specific to a customer or VPN and are not shared, which means each customer has a unique VRF table.